Product Display
The mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) evaporator uses a high-efficiency steam compressor to compress the secondary steam generated by evaporation, convert electrical energy into thermal energy, increase the enthalpy of the secondary steam, and inject the secondary steam with increased thermal energy into the evaporation chamber for heating, in order to achieve the purpose of circulating and utilizing the existing thermal energy of the secondary steam without the need for external fresh steam, and achieve the purpose of evaporation and concentration through self circulation of the evaporator.
Control system temperature, pressure, and motor speed through PLC, industrial computer (FA), configuration, and other forms to maintain system evaporation balance. In theory, using an MVR evaporator saves over 80% of energy, over 90% of condensate water, and reduces footprint by over 50% compared to a traditional evaporator.
working principle
The basic principle of MVR is to improve the cleanliness and enthalpy of waste heat steam generated during the evaporation process through countercurrent washing and mechanical recompression, and reuse it to achieve energy-saving and environmental protection goals.
MVR compressors can use centrifugal compressors or Roots compressors. These machines have a higher volumetric flow rate within the compression ratio range of 1:1.2 to 1:2. The evaporation equipment is compact, occupies a small area, and requires less space. It can also eliminate the need for a cooling system. For existing factories that require expansion of evaporation equipment and insufficient space for steam supply, especially in situations where low-temperature evaporation requires condensation of chilled water, both investment savings and good energy-saving effects can be achieved.
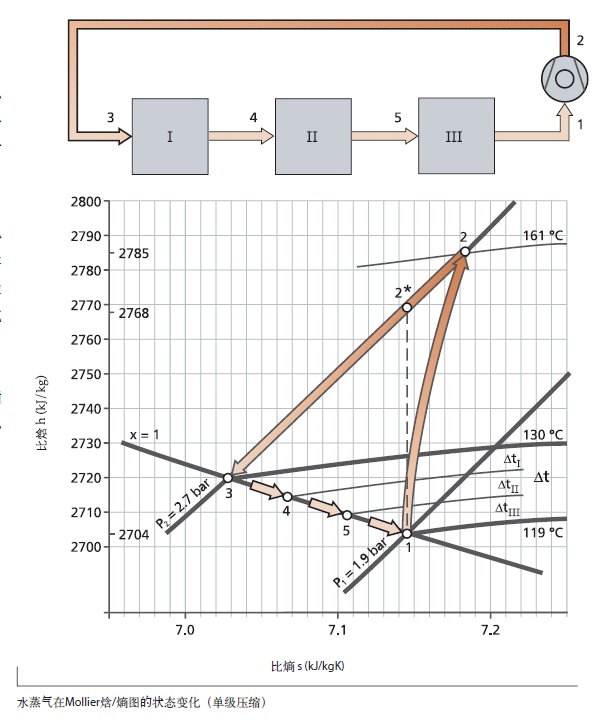
For example, in the above figure, saturated water vapor from the evaporator is compressed from point P1=1.9 bar and T1=119 ℃ in the suction state to P2=2.7 bar and T2=161 ℃, with a compression ratio of 1.4. Compress along the variable curve 1-2.
Performance characteristics
MVR does not generate any steam during the entire evaporation process except for start-up (some materials have low incoming temperatures and require a small amount of steam to preheat to boiling point). In the process of multi effect evaporation, one effect of the evaporator must be given additional heat source energy to increase its temperature (pressure); The steam jet pump (TVR) can only compress a portion of the secondary steam. The MVR evaporator can recycle all the secondary steam in the evaporator. Evaporating one ton of water requires 25-70 kWh of electricity, and the economic efficiency of steam production is equivalent to 20-30 kWh of multi effect evaporation, reducing the demand for external heating and cooling resources, lowering energy consumption, and reducing pollution.
Energy consumption comparison:
Compare the evaporation of a sodium chloride solution with an evaporation rate of 5t/h and a salt content of 10%:
消耗 工藝 | 運行功率 (kW) | 蒸汽消耗 (t/h) | 運行費用 (元/h) | 備注 |
單效蒸發(fā) | 17.6 | 6.0 | 912 | 計電價0.7元/kW?h 蒸汽150元/t |
三效蒸發(fā) | 17.6 | 2.0 | 312 | |
MVR蒸發(fā) | 210.0 | 0.05 | 155 |
Adapt to materials
MVR evaporators are suitable for low-temperature concentration in industries such as milk, glucose, organic acids, VC, xylose, pharmaceuticals, chemical engineering, biotechnology, environmental engineering, waste liquid recovery, papermaking, and salt production. MVR is suitable for materials with low boiling point increase and small evaporation entrainment.
technical specifications
Select the appropriate compressor form based on processing capacity or material characteristics. Roots or centrifugal methods are commonly used. Choose a suitable evaporation process again, such as single-stage evaporation or multi-stage evaporation. If you need specific technical specifications, you can consult our technical personnel. Consultation hotline 13582111060

 中文(簡體)
中文(簡體)