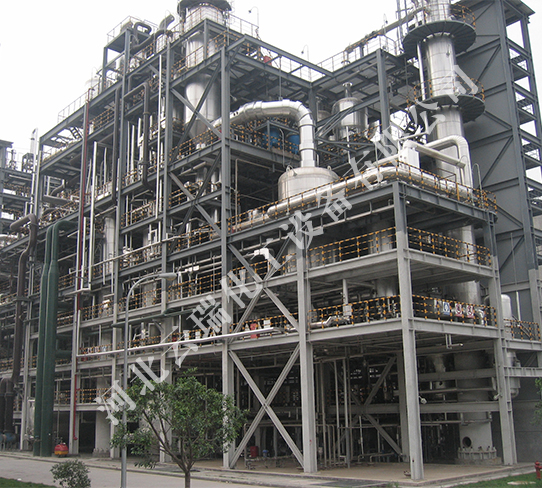
In industrial production processes such as coal chemical, power, and petrochemical, a large amount of wastewater containing inorganic salts is generated. These wastewater have high salt content and belong to high salt wastewater. This type of wastewater cannot be directly biochemically treated, and if discharged directly, it will damage the surrounding soil and water sources. The basic idea for treating high salt wastewater is to separate salt and water with low investment and operating costs, and recycle them separately. In recent years, the application of some new technologies and processes has greatly reduced separation costs, leading to rapid development in the recycling and utilization technology of high salt wastewater.
At present, high salt wastewater is pretreated and membrane concentrated, and then zero discharge of wastewater is achieved through technologies such as MVR evaporation, freeze crystallization, and multi effect evaporation.
Our application examples:
Zero discharge of calcium chloride wastewater from the polycrystalline silicon industry is achieved through membrane concentration and multi effect evaporation.
The sodium chloride wastewater in the chemical industry achieves zero discharge through MVR evaporation and multi effect evaporation.
The concentrated salt water in the coal chemical industry is a mixed salt solution of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate, which is separated by membrane to form two solutions, and then evaporated by MVR, frozen crystallization, and multi effect evaporation to achieve zero emissions.
tower general contractor

 中文(簡(jiǎn)體)
中文(簡(jiǎn)體)