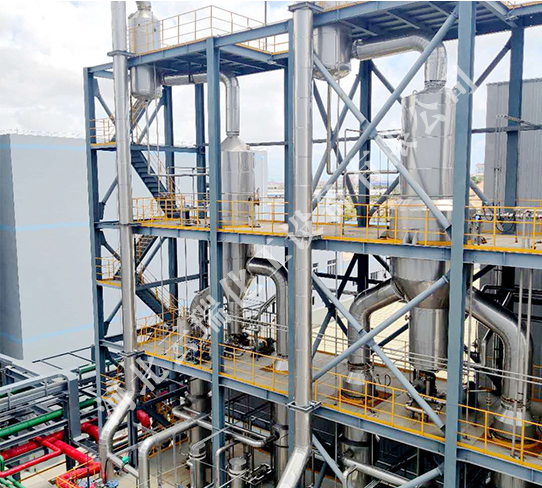
Sodium sulfate is a salt formed by the combination of sulfate ions and sodium ions. Sodium sulfate is soluble in water and its solution is mostly neutral. It is a white, odorless, bitter crystalline or powder with hygroscopicity. The appearance is colorless, transparent, large crystals or granular small crystals. Sodium sulfate is prone to absorbing water when exposed to air, producing decahydrate sodium sulfate, also known as saltpeter, which is slightly alkaline.
The boiling point of sodium sulfate solution does not increase significantly, and relatively pure sodium sulfate wastewater is very suitable for using MVR evaporators. However, due to the solubility characteristics of sodium sulfate, its solubility varies greatly with temperature. When designing the evaporator, anti blocking measures should be considered, and various purging measures should be taken into account in the design of pipelines and systems.
The sodium sulfate MVR evaporator produces no steam throughout the entire evaporation process except for start-up (some materials have low incoming temperatures and require a small amount of steam to preheat to boiling point). Evaporating one ton of water requires 25-70 kWh of electricity, reducing the demand for external heating and cooling resources, lowering energy consumption, and reducing pollution.
tower general contractor

 中文(簡體)
中文(簡體)