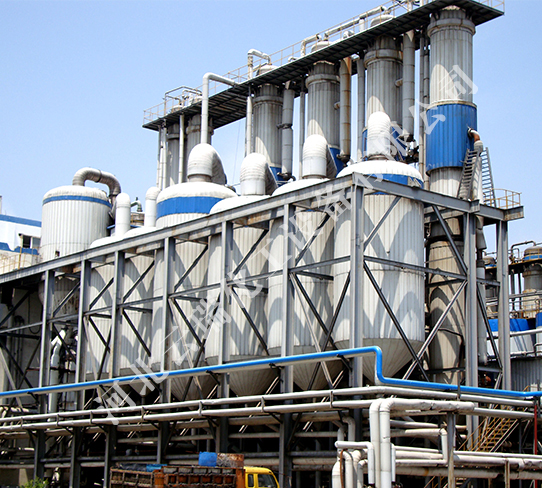
The liquid sugar industry often uses the form of multi effect falling film evaporation, which is widely used for the concentration of aqueous solutions such as glucose, starch sugar, oligosaccharides, maltose, sorbitol, fresh milk, fruit juice, vitamin C, maltodextrin, etc. And it can be widely used for waste liquid treatment in industries such as monosodium glutamate, alcohol, fish meal, etc. Due to the characteristics of the material, more efficient evaporation forms such as four effect, five effect, and six effect are often used to maximize the use of secondary steam. The working principle of the falling film is that the material liquid is added from the tube box on the heating chamber of the falling film evaporator, and is evenly distributed into each heat exchange tube through the liquid distribution and film forming device. Under the gravity of the solution itself, the solution flows down along the inner wall of the heat exchange tube in a uniform film like manner. During the process of flowing down, the heating medium in the shell side heats and vaporizes, and the generated vapor and liquid phase enter the separation chamber of the evaporator together. The vapor and liquid are fully separated, and the vapor enters the condenser for condensation (single effect operation) or enters the next effect as the heating medium, thereby achieving multi effect operation and energy saving. The liquid phase is discharged from the separation chamber.
Main features:
1) The liquid material descends along the inner wall of the tube in a film like manner, and due to the large vaporization surface, there is less liquid foam carried in the steam; When the heat transfer temperature difference is not large, vaporization does not occur on the inner surface of the heating tube, but on the strongly disturbed membrane surface, so scaling is not suitable;
2) The process fluid flows only under the action of gravity, rather than being propelled by high temperature differences, resulting in a small pressure drop and a high heat transfer rate even under low temperature differences, enabling multi effect evaporation under low temperature differences;
3) Easy and convenient to operate, highly adaptable to flow changes, capable of efficient operation over a wide range of flow rates. Evaporation observation can be conveniently conducted through sight glasses and level gauges, and adjustments can be easily made;
4) Suitable for the evaporation of thermosensitive materials, the material can be heated and evaporated only once through the heat exchange tube, and the heating time of the material is short, which can ensure the excellent quality of thermosensitive materials; Under vacuum operation, the quality of thermosensitive materials can be more reliably guaranteed;
5) Strong applicability: Suitable for evaporation operations in the vast majority of media and crystallization operations in low viscosity media; By conveniently adjusting the evaporation temperature, it can meet the requirements of different media for evaporation temperature;
6) Low energy consumption, easy to achieve multi effect operation: the material conveying pump has a small flow rate, low power, and low power consumption; The temperature difference loss of falling film evaporation is small, without the boiling point increase caused by liquid static pressure, and can still ensure a high heat transfer coefficient under small temperature differences (5-7 ℃ temperature difference can also operate normally and efficiently). Therefore, it is easy to achieve multi effect operation under the condition of a constant total heat transfer temperature difference, thus achieving the goal of reducing steam consumption;
7) Due to the film evaporation of the feed liquid in the heating tube of the falling film evaporator, vapor liquid separation is formed. At the same time, at the bottom of the effector, most of the feed liquid is pumped away. Only a small part of the feed liquid and all the secondary steam enter the separator for enhanced separation. The whole process of the feed liquid does not form too much impact, avoiding the formation of foam, which is very suitable for evaporation and concentration of foaming materials.
The liquid sugar industry often uses the form of multi effect falling film evaporation, which is widely used for the concentration of aqueous solutions such as glucose, starch sugar, oligosaccharides, maltose, sorbitol, fresh milk, fruit juice, vitamin C, maltodextrin, etc. And it can be widely used for waste liquid treatment in industries such as monosodium glutamate, alcohol, fish meal, etc. Due to the characteristics of the material, more efficient evaporation forms such as four effect, five effect, and six effect are often used to maximize the use of secondary steam. The working principle of the falling film is that the material liquid is added from the tube box on the heating chamber of the falling film evaporator, and is evenly distributed into each heat exchange tube through the liquid distribution and film forming device. Under the gravity of the solution itself, the solution flows down along the inner wall of the heat exchange tube in a uniform film like manner. During the process of flowing down, the heating medium in the shell side heats and vaporizes, and the generated vapor and liquid phase enter the separation chamber of the evaporator together. The vapor and liquid are fully separated, and the vapor enters the condenser for condensation (single effect operation) or enters the next effect as the heating medium, thereby achieving multi effect operation and energy saving. The liquid phase is discharged from the separation chamber.
Main features:
1) The liquid material descends along the inner wall of the tube in a film like manner, and due to the large vaporization surface, there is less liquid foam carried in the steam; When the heat transfer temperature difference is not large, vaporization does not occur on the inner surface of the heating tube, but on the strongly disturbed membrane surface, so scaling is not suitable;
2) The process fluid flows only under the action of gravity, rather than being propelled by high temperature differences, resulting in a small pressure drop and a high heat transfer rate even under low temperature differences, enabling multi effect evaporation under low temperature differences;
3) Easy and convenient to operate, highly adaptable to flow changes, capable of efficient operation over a wide range of flow rates. Evaporation observation can be conveniently conducted through sight glasses and level gauges, and adjustments can be easily made;
4) Suitable for the evaporation of thermosensitive materials, the material can be heated and evaporated only once through the heat exchange tube, and the heating time of the material is short, which can ensure the excellent quality of thermosensitive materials; Under vacuum operation, the quality of thermosensitive materials can be more reliably guaranteed;
5) Strong applicability: Suitable for evaporation operations in the vast majority of media and crystallization operations in low viscosity media; By conveniently adjusting the evaporation temperature, it can meet the requirements of different media for evaporation temperature;
6) Low energy consumption, easy to achieve multi effect operation: the material conveying pump has a small flow rate, low power, and low power consumption; The temperature difference loss of falling film evaporation is small, without the boiling point increase caused by liquid static pressure, and can still ensure a high heat transfer coefficient under small temperature differences (5-7 ℃ temperature difference can also operate normally and efficiently). Therefore, it is easy to achieve multi effect operation under the condition of a constant total heat transfer temperature difference, thus achieving the goal of reducing steam consumption;
7) Due to the film evaporation of the feed liquid in the heating tube of the falling film evaporator, vapor liquid separation is formed. At the same time, at the bottom of the effector, most of the feed liquid is pumped away. Only a small part of the feed liquid and all the secondary steam enter the separator for enhanced separation. The whole process of the feed liquid does not form too much impact, avoiding the formation of foam, which is very suitable for evaporation and concentration of foaming materials.
tower general contractor

 中文(簡體)
中文(簡體)