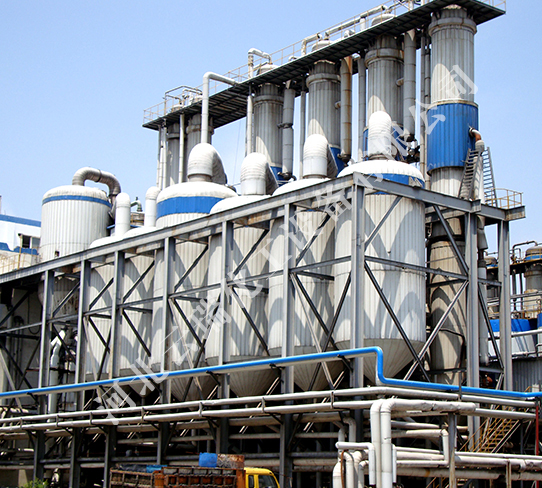
There are various models and specifications of falling film evaporator products, and some can be customized according to customer requirements. The application fields of the products are quite common, which is due to the development trend over many years and the promotion of high-tech. Especially for enterprise products, their characteristics are constantly improving.
The falling film evaporator uses a refrigeration compressor to enhance the kinetic energy of the secondary steam, and applies the enhanced kinetic energy to various aspects of the secondary steam, acquiring the vaporization heat of the secondary steam. In fact, the secondary steam generated by the evaporator is reduced by the insulation of the refrigeration compressor, which increases its working pressure and temperature, and then used as heating steam to be sent into the heating chamber of the evaporator for condensation and heat release reaction. Therefore, the vaporization heat of the steam is recovered and reused.
After being reduced by the steam refrigeration compressor, the secondary steam is sent to the shell side of the falling film heating chamber as heating steam. The shell side of the falling film heating chamber has sections to correctly guide the secondary steam, condense and discharge the uncondensable vapor. The raw materials that need to be evaporated enter from the top of the falling film evaporator through the feeding pump of the falling film evaporator and go through the evaporation tube (tube side). The raw materials are distributed in a thin film form throughout the heat transfer tube according to the falling film evaporator. When the raw materials flow down the tube by attraction, they are heated by the steam inside the tube, reaching the evaporation temperature and causing evaporation. The raw materials flow down from the tube with secondary steam and evaporate in the form of plastic film.
During the entire process of fluidity, the falling film evaporator is heated and vaporized by the shell side heating material, causing the steam to enter the separation chamber of the evaporator together with the high-efficiency liquid phase. The gas-liquid is sufficiently separated, and the steam enters the condenser for condensation (single effect actual operation) or enters the next effect evaporator as the heating material, thereby completing the multi effect actual operation. The high-efficiency liquid phase is discharged from the separation chamber.
Hebei Yunrui Chemical Equipment Co., LtdIndustrial evaporation, crystallization, drying, and
tower general contractor
tower general contractor
National Consultation Hotline:0311-68019522

 中文(簡(jiǎn)體)
中文(簡(jiǎn)體)