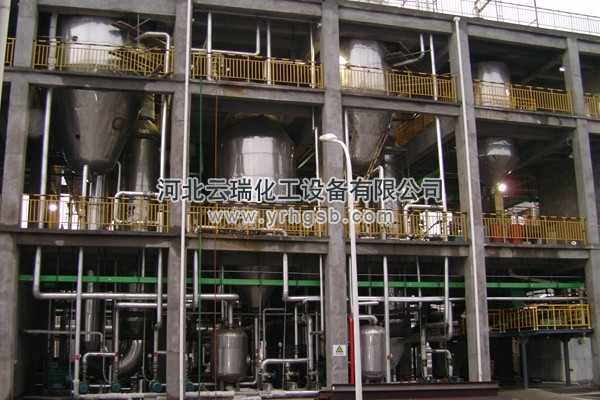
Product Display
Zinc sulfate, also known as alum, is a colorless or white orthorhombic crystal or powder at room temperature. It has astringency and is easily soluble in water. The aqueous solution is acidic and slightly soluble in ethanol and glycerol. Pure zinc sulfate does not turn yellow when stored in air for a long time, but loses water and becomes a white powder when placed in dry air. There are various hydrates: the stable hydrate in equilibrium with the aqueous phase within the range of 0-39 ℃ is zinc sulfate heptahydrate, zinc sulfate hexahydrate within 39-60 ℃, and zinc sulfate monohydrate within 60-100 ℃. Due to salt precipitation during the evaporation process, forced circulation evaporators are often used. In order to meet energy-saving requirements, three effect or multi effect evaporators are often used. Depending on product requirements, downstream, upstream, or mixed flow processes are used to extract products with different crystal waters.
working principle
Forced circulation evaporator: The circulation of solution in the equipment mainly relies on the forced flow generated by external power. The raw material liquid is pumped from bottom to top by a circulation pump, flows upward along the inner tube of the heating chamber, and then undergoes vapor-liquid separation in the separation chamber. The steam is discharged from the upper part, while the liquid is discharged from the bottom of the separation chamber and enters the heating chamber through the circulation pump for further evaporation. The circulation speed has been greatly accelerated, and the size of the circulation speed can be controlled by adjusting the flow rate of the pump. Generally, the circulation speed is between 1.5-2.5m/s.
Performance characteristics
Zinc sulfate will undergo salt precipitation during the evaporation process. Depending on the product requirements, it can be produced into zinc sulfate monohydrate and zinc sulfate heptahydrate.
Adapt to materials
Zinc Sulphate Monohydrate
Zinc sulfate heptahydrate
tower general contractor

 中文(簡體)
中文(簡體)