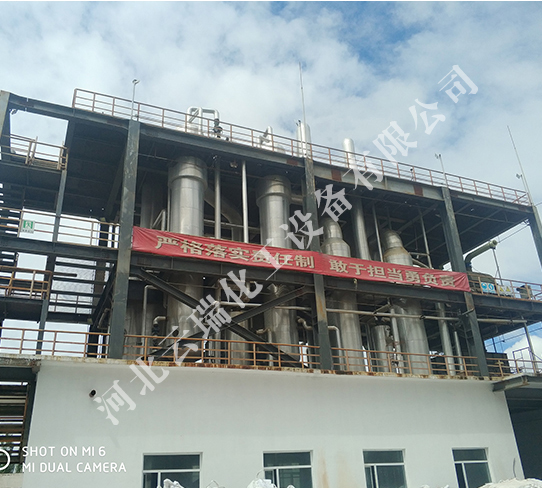
Multi effect evaporator uses the secondary steam generated by the previous effect as the heating steam for the subsequent effect, allowing the heat to be utilized multiple times and using much less steam than single effect evaporation.
In industrial production, it is common to encounter the requirement to process a large amount of liquid and vaporize a large amount of water. In order to save heating steam, multi effect evaporation can be used. Multi effect evaporation is a system that connects multiple evaporators end-to-end and operates in series. The operating pressure and boiling point of the solution in the latter effect are lower than those in the former effect. Only fresh heating steam is added to the first effect with the highest operating pressure, and the generated secondary steam is passed into the heating chamber of the latter effect as the heating steam of the latter effect. That is to say, the heating chamber of the latter effect becomes the condenser of the secondary steam of the former effect. The last effect is often operated under vacuum, and only the secondary steam of the last effect is condensed with a cooling medium. Therefore, multi effect evaporation not only significantly reduces The consumption of heating steam also significantly reduces the consumption of cooling water.
Multi effect countercurrent evaporator refers to the process of materials being opposite to that of secondary steam. The material enters from the final effect, and the concentrated material is extracted from the first effect.
Compared to multi effect co current evaporators, multi effect counter current evaporators have energy-saving advantages, low steam consumption, and the material can be preheated step by step, maximizing the utilization of secondary steam.
tower general contractor

 中文(簡(jiǎn)體)
中文(簡(jiǎn)體)