Evaporation can be carried out under normal pressure, pressure or pressure reduction. Evaporation under reduced pressure is called vacuum evaporation, and the boiling point of a solution decreases below atmospheric pressure, thus increasing the effective heat transfer temperature difference.
Multi effect evaporator uses the secondary steam generated by the previous effect as the heating steam for the subsequent effect, allowing the heat to be utilized multiple times and using much less steam than single effect evaporation.
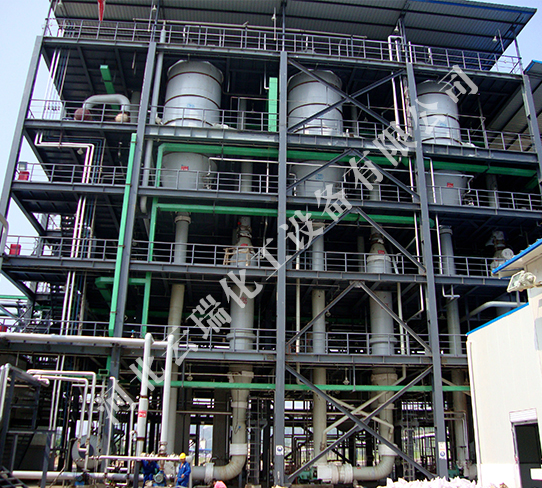
In industrial production, it is common to encounter the requirement to process a large amount of liquid and vaporize a large amount of water. In order to save heating steam, multi effect evaporation can be used. Multi effect evaporation is a system that connects multiple evaporators end-to-end and operates in series. The operating pressure and boiling point of the solution in the latter effect are lower than those in the former effect. Only fresh heating steam is added to the first effect with the highest operating pressure, and the generated secondary steam is passed into the heating chamber of the latter effect as the heating steam of the latter effect. That is to say, the heating chamber of the latter effect becomes the condenser of the secondary steam of the former effect. The last effect is often operated under vacuum, and only the secondary steam of the last effect is condensed with a cooling medium. Therefore, multi effect evaporation not only significantly reduces The consumption of heating steam also significantly reduces the consumption of cooling water.
Multi effect forced evaporator is an efficient circulating evaporation device. The circulation of the solution inside the equipment mainly relies on the forced flow generated by external power, and the circulation speed can generally reach 1.5-5 meters per second. When the circulating liquid flows through the heat exchanger and is heated, it partially evaporates when the pressure drops in the separator, that is, the liquid is cooled to the boiling point temperature at the corresponding pressure. Due to the circulation pump, the material's recirculation speed can be precisely adjusted, and the evaporation rate is set within a certain range. In crystallization applications, crystals can be separated from the circulating slurry by adjusting the circulation flow rate and using special separator designs. The advantage of a forced circulation evaporator is that it has a high heat transfer coefficient and is suitable for processing materials with high viscosity, easy scaling, easy crystallization, or solutions with high concentration. Our company has designed the optimal parameters for the evaporation of secondary steam from the liquid surface of the medium in the separation chamber, and determined the appropriate aspect ratio to ensure that the circulating solution enters the separation chamber and passes through the feed baffle, conical separator, bottom racemizer, top high-efficiency demister, etc., while maintaining the recirculation state internally.
tower general contractor

 中文(簡體)
中文(簡體)